GitHub Enterprise Server compatible agents with Copilot CLI
An example of using the new GitHub Copilot CLI to re-create the GitHub.com Coding and Reviewer Agents within the GitHub Enterprise Server platform
In my article on Six Agentic Dev fundamentals, I mentioned that GitHub Copilot CLI unlocks new use cases for scheduled or event-driven agent tasks. Let’s explore that more with a real implementation: by re-creating GitHub’s Coding and Reviewer Agents to work within a GitHub Enterprise Server environment.
GitHub Enterprise Cloud’s Copilot Coding Agent remains the easiest way to get started with unattended agents. Simply assign a GitHub issue to Copilot, and it works autonomously to create a pull request with the implementation.
But what about organizations blocked from hosting code on SaaS Cloud today for regulatory reasons?
There are many customers globally across Public Sector, Financial Services or other industries who use GitHub Enterprise Server (GHES) or similar self-hosted platforms to securely store code repositories within their own cloud tenant or datacenter. Today they miss out on the ability to leverage unattended agents within their GitHub environment, and must instead assign work via an IDE such as Visual Studio Code.
Creating a GHES Coding Agent
By combining the GitHub CLI, Copilot CLI and GitHub Actions runtime, it’s possible to re-create a similar Coding and Reviewer Agent experience as you see on GitHub.com today, but running within the GHES environment. You can try this out today by cloning my GHES_CodingAgent repository.
The workflow is simple:
- Create a GitHub Issue describing what you want Copilot to work on
- Add a
copilotlabel to the issue (this replaces the ‘Assign to Copilot’ step in GitHub.com) - Watch as Copilot generates code, creates a branch, and opens a PR
All of this happens automatically through GitHub Actions, with no human supervision required.
Important note: Because the Copilot CLI still leverages the same cloud-hosted Copilot API and LLMs, this is not a suitable solution for organizations requiring full data sovereignty on all IT systems. But for those who already leverage the GitHub Copilot service today via the IDE, this is an interesting approach to bring unattended agents directly into the GHES platform.
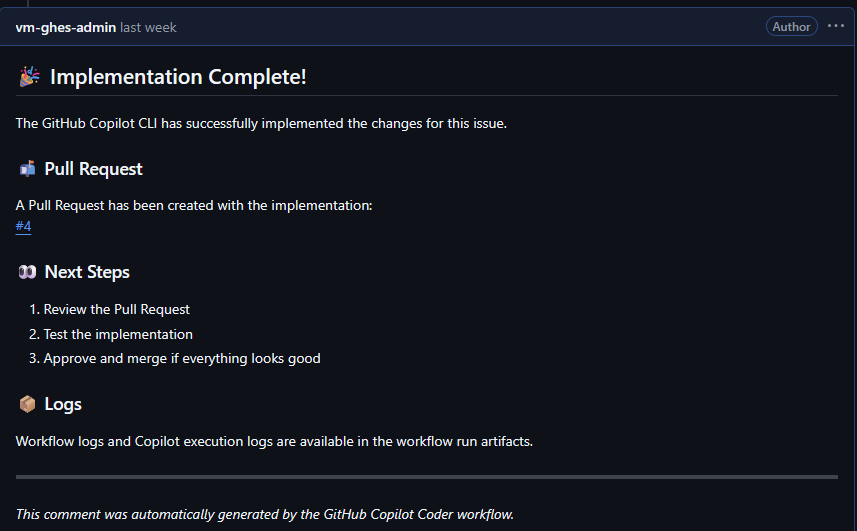
Example output from the CLI Coding Agent
How Copilot CLI powers the workflow
The magic here is GitHub Copilot CLI, which brings the same AI capabilities you use in an IDE to the command line. It allows you to run Copilot in any automated pipeline or script.
Here’s what typical unattended usage looks like:
gh copilot -p "$ISSUE_DESCRIPTION" --mcp-config mcp-config.json
The CLI takes your prompt (in this case, the GitHub issue description), processes it with the same AI models that power Copilot in your IDE, and executes the coding task autonomously.
Building reusable workflows for scale
One of the challenges with rebuilding a core GitHub.com service in Actions/CLI was how to scale properly across multiple repos. Maintaining local copies of YAML scripts in every repo isn’t ideal, so the current prototype uses a hub-and-spoke model:
Central Repo (GHES_CodingAgent)
├── Master workflows with full logic
├── MCP configuration
└── Deployment script to deploy workflows to a target repo
Target Repos
└── Lightweight caller workflows (~30 lines each)
Because the target repos reference logic from the master workflows, update the central repo once and all connected repos get the improvements automatically.
Automated PR reviews
The same project also includes a Copilot Reviewer Agent that analyzes pull requests on-demand. Add the same copilot label to any PR, and the reviewer workflow:
- Downloads all changed files
- Runs code review using the Copilot CLI
- Posts actionable review comments directly on the PR
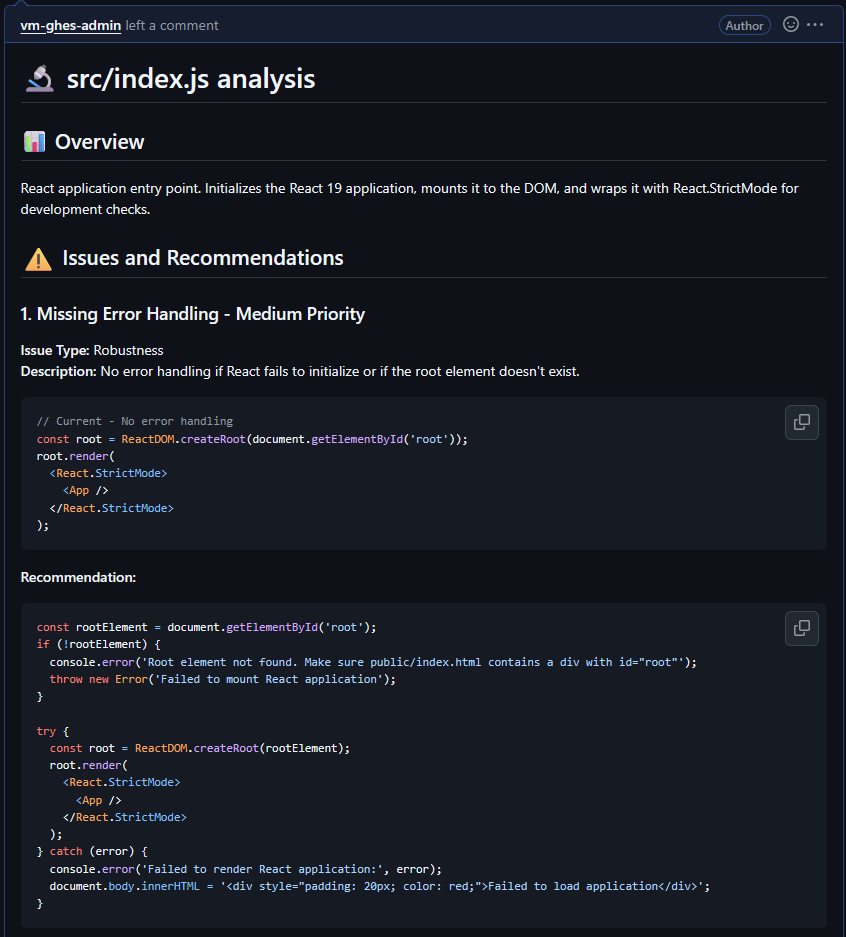
Example output from the CLI Reviewer Agent
Getting started
The full project is available on GitHub with detailed setup instructions. You’ll need:
- GitHub Enterprise Server with GitHub Actions runners deployed
- A GitHub Copilot license for the user who will setup the agents
- Personal Access Tokens for both GHES and GitHub Copilot, which the CLI uses to authenticate on your behalf
From there, it’s a matter of configuring secrets and deploying the workflow to your target repositories.
Final thoughts
Copilot CLI represents an exciting evolution in how we think about AI-assisted development. Moving from “AI helps me code” to “AI codes while I review” is a significant shift, and having the CLI available means you can orchestrate this in creative ways that fit your specific environment and workflows.
If you’re on GHES and want to start integrating agents into your existing workflows, this approach might be exactly what you need.
Try it now at: GHES_CodingAgent.
Happy automating! 🤖
